ArangoGraph Now Available on AWS Marketplace
Estimated reading time: 1 minute
Today we are excited to announce that ArangoGraph, the ArangoDB Managed Service, is available for purchase in the AWS Marketplace. With this announcement, ArangoGraph can now be purchased directly via both AWS and GCP.
The AWS Marketplace provides an extensive catalog of software solutions for users to easily explore, test, buy, and deploy on AWS. If you’re an AWS customer, here’s what this announcement means for you:
(more…)Introducing the ArangoDB-DGL Adapter
Estimated reading time: 15 minutes
We are proud to announce the GA 1.0 release of the ArangoDB-DGL Adapter!
The ArangoDB-DGL Adapter exports Graphs from ArangoDB, a multi-model Graph Database, into Deep Graph Library (DGL), a python package for graph neural networks, and vice-versa.
(more…)Introducing the ArangoDB-NetworkX Adapter
Estimated reading time: 18 minute
We are proud to announce the GA 3.0 release of the ArangoDB-NetworkX Adapter!
The ArangoDB-Networkx Adapter exports Graphs from ArangoDB, a multi-model Graph Database, into NetworkX, the swiss army knife for graph analysis with python, and vice-versa.
(more…)Announcing ArangoDB Series B Funding
Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
This blog post is to announce ArangoDB’s Series B funding round and provide an update on the progress we have made so far. The company has achieved a lot in the past couple of years since we announced our Series A round of funding in 2019. We are excited for what lies ahead and can’t wait to bring you along for the journey!

Take Alpha 2 of the upcoming ArangoDB 3.7 for a spin!
Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
We are 11 weeks into the development of ArangoDB 3.7 and want to give you yet another opportunity to try out the upcoming features before the release. On our technical preview page, you’ll find the Alpha 2 packages for the Community and Enterprise Edition.
This Alpha 2 comes with pretty neat features and improvements and we hope to get your early feedback!
This is particularly helpful for us to adjust our development in terms of solving real-world problems for you and ease-of-use for the new capabilities like: Read more
Alpha 1 of the upcoming ArangoDB 3.7
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
We released ArangoDB version 3.6 in January this year, and now we are already 6 weeks into the development of its follow-up version, ArangoDB 3.7. We feel that this is a good point in time to share some of the new features of that upcoming release with you!
We try not to develop new features in a vacuum, but want to solve real-world problems for our end users. To get an idea of how useful the new features are, we would like to make alpha releases available to everyone as soon as possible. Our goal is get early user feedback during the development of ArangoDB, so we can validate our designs and implementations against the reality, and adjust them if it turns out to be necessary.
If you want to give some of the new features a test drive, you can download the 3.7 Alpha 1 from here – Community and Enterprise – for all supported platforms. Read more
What’s new in ArangoDB 3.6: OneShard Deployments and Performance Improvements
Estimated reading time: 9 minutes
Welcome 2020! To kick off this new year, we are pleased to announce the next version of our native multi-model database. So here is ArangoDB 3.6, a release that focuses heavily on improving overall performance and adds a powerful new feature that combines the performance characteristics of a single server with the fault tolerance of clusters.
If you would like to learn more about the released features in a live demo, join our Product Manager, Ingo Friepoertner, on January 22, 2020 - 10am PT/ 1pm ET/ 7pm CET for a webinar on "What's new in ArangoDB 3.6?".
Need to know more about multi-model?
tl;dr: Highlights of ArangoDB 3.6:
- OneShard Feature
- Performance Optimizations
- Subquery acceleration (up to 30x)
- Late document materialization
- Early pruning of non-matching documents
- Parallel AQL execution in clusters
- Streamlined update and replace queries
- ArangoSearch Enhancements
- New Cloud Service Pricing Model
ArangoDB 3.6 is also available on ArangoDB ArangoGraph - the cloud service for ArangoDB. Start your free 14-day trial today!
You will not regret upgrading to 3.6, as it most likely will improve your experience with your existing ArangoDB setup.
In 3.6 we concentrated strongly on performance optimizations for the everyday use of ArangoDB, and we picked the ones with the biggest impact first. As many users as possible should experience notable improvements and there is more in the pipeline for future releases.
Subquery performance has been improved up to 30 times, parallel execution of AQL queries allow to significantly reduce gathering time of data distributed over several nodes, and late document materialization reduces the need to retrieve non-relevant documents completely. Simple UPDATE and REPLACE operations that modify multiple documents are more efficient because several processing steps have been removed. The performance package is rounded off by an early pruning of non matching documents, essentially by directly applying the filter condition when scanning the documents, so that copying documents that do not meet the filter condition into the AQL scope can be avoided. Read more details in the AQL Subquery Benchmark or in the feature descriptions further on in this blog post.
The feature with probably the greatest impact is OneShard. Available in the Enterprise Edition of ArangoDB, customers can run use cases such as Graph Analytics on a single database node, with high availability and synchronous replication. Because the data is not distributed across multiple nodes, the graph traversal can be efficiently performed on a single node. The OneShard Cluster deployments are also available from our managed service, ArangoDB ArangoGraph.
With every release, we also improve the capabilities of ArangoSearch, our integrated full-text search engine with ranking capabilities. In 3.6 we have added support for edge n-grams to the existing Text Analyzer to support word-based auto-completion queries, improved the n-gram Analyzer with UTF-8 support and the ability to mark the beginning/end of the input sequence. ArangoSearch now also supports expressions with array comparison operators in AQL, and the `TOKENS()` and `PHRASE()` functions accept arrays. Both features enable dynamic search expressions.
If you are working with Dates you should know that AQL in 3.6 enforces a valid date range for working with date/time in AQL. This restriction allows for faster date calculation operations.
Of course, there are many other small features and improvements under the hood that you can leverage, please have a look at the Release Notes and the Changelog for all details.
ArangoDB 3.6 is already available on our Managed Cloud Service ArangoDB ArangoGraph, which offers you enterprise-quality ArangoDB clusters on AWS, Google Compute and soon Azure as well. Take ArangoDB 3.6 for a spin there with just a few clicks. First 14 days are on us!
New Cloud Service Pricing Model
In parallel to the 3.6 release, we are pleased to introduce also a new, attractive pricing system for ArangoDB ArangoGraph. You can now have your own highly available and scalable deployment from as little as $0.21 per hour (3 nodes, 4 GB RAM & 10 GB memory).
Some sample configurations for a 3-node OneShard deployment and their starting prices are listed in the table below (Please find the exact price for your desired setup within your ArangoGraph Account).
| Memory per node | Storage per node | Starting at |
| 4GB | 10GB | $0.21/hour |
| 8GB | 20GB | $0.52/hour |
| 16GB | 40GB | $0.91/hour |
| 32GB | 80GB | $1.74/hour |
| 64GB | 160GB | $3.42/hour |
| 128GB | 320GB | $6.52/hour |
The team worked very hard to further reduce the footprint of ArangoGraph sidecars, optimize the use of cloud resources and automate the modern ArangoGraph deployment process. In addition, we have been able to ramp up far more customers than expected in recent weeks, allowing us to pass on lower cloud costs and add support for more regions.
We hope that ArangoGraph is now an even better solution for more in the community and will continue to drive prices down further.
Register for the Webinar "What's new in ArangoDB 3.6" on January, 22nd, 2020 - 10am PT/ 1pm ET/ 7pm CET to see a live demo of newly released features.
For those who are curious what the features are about, here are some highlights with a brief description:
OneShard (Enterprise Edition)
Not all use cases require horizontal scalability. In such cases, a OneShard deployment offers a practicable solution that enables significant performance improvements by massively reducing cluster-internal communication.
 A database created with OneShard enabled is bound to a single DB-Server node but still replicated synchronously on other nodes to ensure resilience. This configuration allows running transactions with ACID guarantees on shard leaders.
A database created with OneShard enabled is bound to a single DB-Server node but still replicated synchronously on other nodes to ensure resilience. This configuration allows running transactions with ACID guarantees on shard leaders.
This setup is highly recommended for most Graph use cases and join-heavy queries.
If an AQL query accesses only collections that are locally on the same DB-Server node, the whole execution is transferred from the Coordinator to the DB-Server.
The possibilities are a lot broader than this, so please continue to read more about multi-tenancy use cases, ACID transactions and mixed-mode in the OneShard documentation.
Early pruning of non-matching documents
ArangoDB 3.6 evaluates `FILTER` conditions on non-index attributes directly while doing a full collection scan or an index scan. Any documents that don't match the `FILTER` conditions will then be discarded immediately.
Previous versions of ArangoDB needed to copy the data of non-matching documents from the scan operation into some buffers for further processing and finally filtering them.
With this scanning and filtering now happening in lockstep, queries that filter on non-index attributes will see a speedup. The speedup can be quite substantial if the `FILTER` condition is very selective and will filter out many documents, and/or if the filtered documents are large.
For example, the following query will run about 30 to 50% faster in 3.6 than in 3.5:
FOR doc IN collection
FILTER doc.nonIndexedValue == "test123456"
RETURN doc
(Mileage may vary depending on actual data, the tests here were done using a single server deployment with the RocksDB storage engine using a collection with one million documents that only have a single (non-indexed) `nonIndexedValue` attribute with unique values).
Subquery Performance Optimization
Subquery splicing inlines the execution of certain subqueries using a newly introduced optimizer rule. On subqueries with few results per input, the performance impact is significant.
Here is a self-join example query:
FOR c IN colC
LET sub = (FOR s IN colS FILTER s.attr1 == c.attr1 RETURN s)
RETURN LENGTH(sub)
Inlining this basic subquery yields to 28x faster query execution time in a cluster setup and a collection of 10k documents.
Explore further details in his Subquery Performance Benchmark.
Late document materialization (RocksDB)
Queries that use a combination of `SORT` and `LIMIT` will benefit from an optimization that uses index values for sorting first, then applies the `LIMIT`, and in the end only fetches the document data for the documents that remain after the `LIMIT`.
Sorting will be done on the index data alone, which is often orders of magnitude smaller than the actual document data. Sorting smaller data helps reducing memory usage and allocations, utilize caches better etc. This approach is often considerably faster than fetching all documents first, then sorting all of them using their sort attributes and then discarding all of them which are beyond the `LIMIT` value.
Queries, as follows, could see a substantial speedup:
FOR doc IN collection
FILTER doc.indexedValue1 == "test3"
SORT doc.indexedValue3
LIMIT 100
RETURN doc
The speedup we observed for this query is about 300%. For other queries we have seen similar speedups.
(Mileage may vary depending on actual data, the tests here were done using a single server deployment with the RocksDB storage engine using a collection with one million documents and a combined index on attributes `indexedValue1`, `indexedValue2` and `indexedValue3`. There were 10 distinct values for `indexedValue1`).
That optimization is applied for collections when using the RocksDB storage engine and for ArangoSearch views.
Parallel Execution of AQL Queries
ArangoDB 3.6 can parallelize work in many cluster AQL queries when there are multiple database servers involved. For example, if the shards for a given collection are distributed to 3 different database servers, data will be fetched concurrently from the 3 database servers that host the shards' data. The coordinator will then aggregate the results from multiple servers into a final result.
Querying multiple database servers in parallel can reduce latency of cluster AQL queries a lot. For some typical queries that need to perform substantial work on the database servers we have observed speedups of 30 to 40%.
The actual query speedup varies greatly, depending on the cluster size (number of database servers), number of shards per server, document count and size, plus result set size.
Parallelization is currently restricted to certain types of queries. These restrictions may be lifted in future versions of ArangoDB.
Optimizations for UPDATE and REPLACE queries
Cluster query execution plans for simple `UPDATE` and `REPLACE` queries that modify multiple documents and do not use `LIMIT` will now run more efficiently, as the optimizer can remove several execution steps automatically. Removing these steps reduces the cluster-internal traffic, which can greatly speed up query execution times.
For example, a simple data-modification query such as:
FOR doc IN collection
UPDATE doc WITH { updated: true } IN collection
Here we could remove one intermediate hop to the coordinator, which also makes the query eligible for parallel execution. We have seen speedups of 40% to 50% due to this optimization, but the actual mileage can vary greatly depending on sharding setup, document size and capabilities of the I/O subsystem.
The optimization will automatically be applied for simple `UPDATE`, `REPLACE` and `REMOVE` operations on collections sharded by `_key` (which is the default), provided the query does not use a `LIMIT` clause.
ArangoSearch Enhancements
We continuously improve the capabilities of ArangoSearch. The late document materialization mentioned accelerates the search by reading only necessary documents from the underlying collections.
Search conditions now support array comparison operators with dynamic arrays as left operand:
LET tokens = TOKENS("some input", "text_en") // ["some", "input"]
FOR doc IN myView SEARCH tokens ALL IN doc.title RETURN doc // dynamic conjunction
FOR doc IN myView SEARCH tokens ANY IN doc.title RETURN doc // dynamic disjunction
FOR doc IN myView SEARCH tokens NONE IN doc.title RETURN doc // dynamic negation
FOR doc IN myView SEARCH tokens ALL > doc.title RETURN doc // dynamic conjunction with comparison
FOR doc IN myView SEARCH tokens ANY <= doc.title RETURN doc // dynamic disjunction with comparison
In addition, the `TOKENS()` and `PHRASE()` function can be used with arrays as parameter. For more information on the array support, see the release notes.
In ArangoDB 3.6 we have added edge n-gram support to the Analyzer type `text` of ArangoSearch. For each token (word) `edge n-grams` are generated. This means that the beginning of the `n-gram` is anchored to the beginning of the token, while the `ngram` analyzer would generate all possible substrings from a single input token (within the defined length restrictions).
Edge n-grams can be used to cover word-based auto-completion queries with an index.
UTF-8 support and the ability to mark the start/end of the sequence for the `n-gram` Analyzer type have been added. The marker is appended to `n-grams` and allows searching for these positions in tokens.
Example Analyzer and Query:
arangosh>analyzer.save("myNgram", "ngram", { min:2, max:3, startMarker: "^", endMarker: "$", streamType: "utf8"})
FOR d IN view x
SEARCH ANALYZER(d.category == "^new", "myNgram")
The marker "^" now restricts category results to those that begin with "new".
Take ArangoDB 3.6 for a test drive. Any feedback is, as always, highly appreciated! If you are upgrading from a previous version, check our General Upgrade Guide.
Join the “What is new in ArangoDB 3.6?” webinar to get a hands-on overview on the new features with our Product Manager, Ingo Friepoertner, on January 22, 2020 - 10am PT/ 1pm ET/ 7pm CET.
We hope you find many useful new features and improvements in ArangoDB 3.6. If you like to join the ArangoDB Community, you can do so on GitHub, Stack Overflow and Slack.
Continue Reading
Performance analysis with pyArango: Part II
Inspecting transactions
Release Candidate 2 of the ArangoDB 3.6 available for testing
We are working on the release of ArangoDB 3.6 and today, just in time for the holiday season, we reached the milestone of RC2. You can download and take the RC2 for a spin: Community Edition and Enterprise Edition.
The next version of the multi-model database will be primarily focused on major performance improvements. We have improved on many fronts of speeding up AQL and worked on things like:
- Subquery performance
- Parallel execution of AQL queries that allows to significantly reduce gathering time of data distributed over several nodes
- Late document materialization that reduces the need to retrieve non-relevant documents completely
- `UPDATE` and `REPLACE` operations
- Early pruning of non matching documents that directly applies the filter condition when scanning the documents, so that copying documents that do not meet the filter condition into the AQL scope can be avoided
The new feature that will be generally available with ArangoDB 3.6 Enterprise Edition is OneShard.
Not all use cases require horizontal scalability. In such cases, a OneShard deployment offers a practicable solution that enables significant performance improvements by massively reducing cluster-internal communication. A database created with OneShard enabled is limited to a single DB-Server node but still replicated synchronously to ensure resilience. This configuration allows running transactions with ACID guarantees on shard leaders.
Read more about this feature in our documentation. You can already try out the benefits of OneShard by testing the Enterprise Edition Release Candidate 2. If you have ArangoDB installed, please remember to backup your data and run an upgrade after installing the RC release.
With every release of ArangoDB, we are continuously working on improvements in ArangoSearch - our full-text search engine including similarity ranking capabilities. With the upcoming ArangoDB 3.6 we have added support for edge n-grams to the existing Text Analyzer to support word-based auto-completion queries. The n-gram Analyzer was also enhanced with UTF-8 support and the ability to mark the beginning/end of the input sequence. Two new features that enable dynamic search expressions were also added: the `TOKENS()` and `PHRASE()` functions accept arrays and expressions with array comparison operators in AQL.
For the full list of features and improvements that are going to be introduced with the upcoming ArangoDB 3.6 check out the Release Notes or the Changelog.
Happy testing and it would be fantastic to hear about your feedback via Github.
Say Hi To ArangoDB ArangoGraph: A Fully-Managed Multi-Model Database Service
 After two years of planning, preparation and a few lines of code, you can now enjoy an even more comfortable developers' life with ArangoDB.
After two years of planning, preparation and a few lines of code, you can now enjoy an even more comfortable developers' life with ArangoDB.
Today, we are happy to announce the launch of ArangoDB’s managed service Oasis – a fully-managed graph database, document, and key-value store, as well as a full-text search engine – in one place.
Oasis is available immediately for Google Cloud, AWS – and also Microsoft Azure will be available very soon.
The goal for Oasis was and is to provide highly scalable and secure deployments with just a few clicks and to be ready for action in minutes. And this is exactly what Oasis is.
Take ArangoDB Oasis for a test run. Feel free to sign-up for your free 14-day trial by just creating your account here: cloud.arangodb.com.
ArangoDB Oasis in a Nutshell
ArangoDB Oasis offers everything you can expect from a modern managed service offering. And, as it runs a native multi-model database, you get a managed, scalable document store, graph database and search engine in one place.
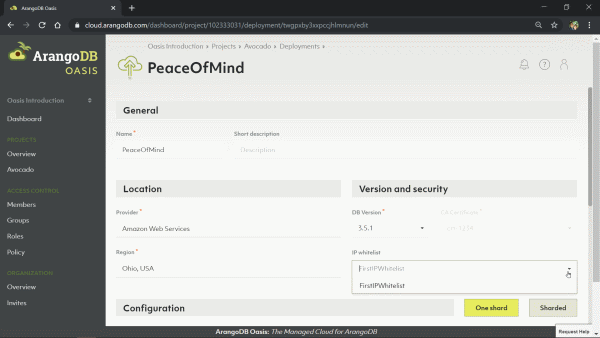
Per default, Oasis runs the Enterprise Edition of ArangoDB, including security features like encryption (on transit, at rest, backups) and auditing, but also the special enterprise features like SmartGraphs and SmartJoins. These features enable high performance even with complex query requirements on distributed datasets.
Elastic Scalability
Creating deployments on ArangoDB Oasis is really simple. Just select your preferred cloud provider and region, configure your deployment and hit “create”. Oasis will send you a notification as soon as your deployment is ready for action.
Application needs change over time and a managed service should meet those changing requirements. You can easily define and change the size of your database nodes as well as the amount of instances you want in your deployments without any service interruption. Oasis takes care of everything under the hood.
Enterprise-Grade Security
Our Oasis team lead and architect Ewout likes to say, “We are living in 2019, so security should be prio 1. Always.” To ensure that you can build your applications to very high-security standards, Oasis always encrypts everything before it hits the disk.
From HTTPS endpoints to encryption at rest and encrypted backups (AES-256-CTR encryption), your data is safe. ArangoDB Oasis also provides fine-grained role-based access control and policies, so you can clearly define who has access to what on an organization, project and individual deployment level.
IP-Whitelisting, internal firewalls, auditing and enhanced data masking for data exports are also included to build HIPAA-, PCI- and GDPR/CCPA-compliant applications on top of Oasis.
OneShard: Highly-Available, Fault-Tolerant & Transactional Deployments
With the launch of Oasis, users now have access to a brand new deployment mode called OneShard.
Especially for graph use cases, many from the community expressed the need of an additional deployment mode for ArangoDB to provide the high-availability and fault-tolerance benefits of a cluster, with the traversal performance and transactional guarantees of a single instance or active failover setup.
The new OneShard deployment provides an ideal solution: synchronous replication and multi-document transactions as well as efficient, locally executed AQLs to speed-up graph traversals and joins. OneShard is the ideal option for applications where all your data fits on one node, where you need to run queries across all data and you, therefore, want to minimize the number of network hops (Graph Traversals, Join Operations) while you rely on synchronous replication to guarantee availability and fault-tolerance.
Organized & Secure Teamwork
When you register for ArangoDB Oasis, you will automatically create your first organization (your account). Each organization can have multiple projects and each project can have multiple deployments.
 This structure mirrors the reality in many corporations and their application development process - for each project you might have a deployment for development, one for staging and one for production. The Oasis structure is also perfectly suitable for freelancers having different clients.
This structure mirrors the reality in many corporations and their application development process - for each project you might have a deployment for development, one for staging and one for production. The Oasis structure is also perfectly suitable for freelancers having different clients.
You can invite new members to your organization just by email and configure user roles and their access policies down to the individual deployment level. Users can also be organized in groups to allow certain access rights for every member of this group.
Fast, Consistent, Schedulable Backups
Whether you have a OneShard setup or a cluster with sharded data, what you want is a fast, simple way to create and restore backups.
With the support of ArangoDB’s “Hot Backup” feature in Oasis, you can create backups either on demand or automatically in configurable intervals like hourly, daily, weekly and so on. Local backups can be restored within a couple of seconds.
Support & Pricing
With ArangoDB Oasis, your organization can belong to one of the following three tiers:
- Free-To-Try: Everyone can have a free deployment on any supported cloud provider for 14 days for testing with basic support.
- Professional: Upgrade your Organization anytime to Professional and create as many deployments as you like. Easily configure the size and resources of your deployments. Much shorter response times for support requests.
- Enterprise: Best available support and response times. For more details contact our Sales Team
The organization is the payroll unit. All deployments are debited from the organization's credit card (you don't need a credit card in the free tier), with invoices that allow costs to be allocated to individual deployments and projects. Each organization can only belong to one Oasis tier (Free, Pro or Enterprise).
The price for your deployment depends on the cloud provider you selected, the amount of nodes and the size of the memory and storage you selected. You can directly see the price for any configuration you select before you create a new deployment or reconfigure an already existing one.
What’s next?
We will improve Oasis constantly but also have two major improvements already on the horizon.
Add support for Microsoft Azure cloud. We are listening to all of your valuable feedback and will add Azure soon.
Missing a region? Let us know! Many regions are already supported and we are more along user & customer feedback. Just open a support ticket in Oasis and let us know about your preferences.
ArangoDB Oasis is an API-driven framework that also allows Oasis to be controlled with various scripts. In the near future, we will also make this API available for users to allow its usage e.g. for continuous integration and deployment needs, or for automated scheduling of deployments.
Get started with Oasis today! Just sign-up and test ArangoDB Oasis for free at cloud.arangodb.com.
ArangoDB 3.5 Released: Distributed Joins & Transactions
We are super excited to share the latest upgrades to ArangoDB which are now available with ArangoDB 3.5. With the fast-growing team, we could build many new and long-awaited features in the open-source edition and Enterprise Edition. Get ArangoDB 3.5 on our download page and see all changes in the Changelog.
Need to know more about multi-model?
Maybe good to know: Our Cloud Service offering, ArangoDB ArangoGraph, will run the full Enterprise Edition of ArangoDB 3.5 including all security as well as special features. You can find more about ArangoDB ArangoGraph and play around for 14-days free in the cloud.
Join the upcoming ArangoDB 3.5 Feature Overview Webinar to have a detailed walkthrough on the release with our Head of Engineering and Machine Learning, Jörg Schad.
tl;dr Highlights of ArangoDB 3.5
- SmartJoins which enable you to run efficient co-located JOIN operations against distributed data (Enterprise Edition)
- The long awaited Streaming Transactions API which lets you run & manage ACID transactions directly from your driver (Java Sync, Go, JavaScript & PHP already supported)
- ArangoSearch improvements including configurable analyzers, lightning fast sorted indexes and other goodies
- Extended graph database capabilities like k-shortest path and the new PRUNE keyword
- Data Masking lets you work securely with obfuscated production data for real-world development & testing environments (Enhanced Data Masking available in Enterprise)
- Helpful updates like Time-To-Live Indexes, Index Hints and Named Indexes
- And a little late to the party… Lightning fast consistent Cluster Backups (following with 3.5.1/ Enterprise-only)
Keen to learn more? Let’s take a closer look at the new features.
SmartJoins - Co-located JOINs in a NoSQL Database
There are many operational and analytical use cases where sharding two large collections is needed, and fast JOIN operations between these collections is an important requirement.
In close teamwork with some of our largest customers, we developed SmartJoins (available in ArangoDB Enterprise only). This new feature allows to shard large collections to a cluster in a way that keeps data to be joined on the same machines. This smart sharding technique allows co-located JOIN operation in ArangoDB many might know from RDBMS but now available in a multi-model NoSQL database.
While our first offering of distributed JOIN operations, SatelliteCollections, allows for sharding one large collection and replicating many smaller ones for local joining, SmartJoins allow two large collections to be sharded to an ArangoDB cluster, with JOIN operations executed locally on the DBservers. This minimizes network latency during query execution and provides the performance close to a single instance for analytical and operational workloads.
For example, let’s assume we have two large collections, e.g. `Products` and `Orders`, which have a one-to-many relationship as each product can appear in any order. You can now use e.g. the `productId` during the creation of the collection to shard the two collections alike (see arangosh example below):
db._create("products", { numberOfShards: 3, shardKeys: ["_key"] });
db._create("orders", { distributeShardsLike: "products", shardKeys: ["productId"] });When querying both collections with your normal join query in AQL, the query engine will automatically recognize that you sharded the data in a SmartJoin-fashion and only send the query to the relevant DB-servers for local query execution. Network overhead is thereby reduced to an absolute minimum.
For more details you can either check out the SmartJoins tutorial or watch the walk through below showing off some first performance indications and how to even combine SmartJoins with SatelliteCollections:
Streaming Transactions API - Execute & Control ACID Transactions From Your Language Driver
ArangoDB supported ACID transactions basically from the very beginning, either via AQL operations or by writing transactions in JavaScript. The new streaming transactions API now allows users to BEGIN, COMMIT or ABORT (rollback) operations from all supported drivers (i.e., Java Sync, GO, JavaScript, PHP).
With the streaming transaction API, a transaction can consist of a series of transactional operations and therefore allows clients to construct larger transactions in a much more efficient way than the previous JavaScript-based solution. You can also leverage various configurations for your transactions to meet your individual needs, like:
- Collections: The collections the transaction will need for any write operation
- waitForSync: An optional boolean flag to force the transaction to write to disk before returning
- allowImplicit: Allows the transaction to read from undeclared collections
- lockTimeout: Lets you specify the maximum time for the transaction to be completed (default is 10 minutes)
- maxTransactionSize: If you are using RocksDB as your storage engine (default engine since ArangoDB 3.4), you can define the maximal size of your transaction in bytes
For more details, please see the documentation for Streaming Transactions. If you are maintaining an ArangoDB driver, please see the RC blogpost for details around integrating the new API into your driver.
Please note: Streaming transactions come with full ACID guarantees on a single instance and provide also a better transactional experience in a cluster setting. ArangoDB does not support distributed ACID transactions -- yet.
Search Engine Upgrades - Configurable Analyzers and Lightning-Fast Sorted Queries
Frankly, we are absolutely thrilled about how many people embrace ArangoSearch and build amazing applications with it. Having a fully integrated C++ based search & ranking engine within a multi-model database seems to come in very handy for many people out there. New to ArangoSearch? Check out the tutorial
We enlarged the ArangoSearch team and can now release two huge improvements to the search capabilities of ArangoDB: Configurable Analyzers & Super Fast Sorted Queries.
Configurable Analyzers let you perform case-sensitive searches, word stemming and also let you use your own language-specific stopword lists. They also let you fine-tune your ArangoSearch queries even better for a broad variety of languages, including English, French, German, Chinese and many more. Check out the tutorial on how to work with Configurable Analyzers in ArangoDB.
Queries including sorting will see a real performance boost in ArangoDB 3.5 when using the new sorted indexes. When creating a `view` for ArangoSearch you can now specify the creation of this new index and define which sort order is best for your queries (asc/dec). If the sort order in your query matches the one specified in your view, results can be directly read from the index and returned super fast. Internal benchmarks show a performance improvement of up to 1500x for these situations.
Creating a sorted view can be done via `arangosh`
db._createView('myView', 'arangosearch', { links : { ... }, primarySort: [ { field: 'myField', direction: 'asc' }, { field: 'anotherField', direction: 'desc' } ] })
db._query('FOR d in myView SEARCH ... SORT d.myField ASC RETURN d`); // no sorting at query time
For more details on Sorted Views & ArangoSearch, check out the video tutorial below:
Additional Upgrades to ArangoSearch
Besides the new key features of ArangoSearch, you can now access and also use the relevance scores calculated by the BM25 or TFIDF algorithms directly in queries to e.g. limit searches to only include results meeting a minimum relevancy to your query.
Restricting search queries to specific collections can provide performance benefits for your queries. If your ArangoSearch `view` spans multiple collections, you can now limit your search queries to specific collections which you can define within your search queries. This can provide a significant performance boost, as less data has to be accessed.
For more details, please see the blog post for ArangoSearch Updates.
Graph Database Upgrades - k-shortest path and new PRUNE keyword
As one of the leading graph databases out there, ArangoDB already provides a rich feature set ranging from simple graph traversals to complex distributed graph processing.
New to graphs?
The new k-shortest path feature adds to this featureset and provides the option to query for all shortest paths between two given vertices, returning sorted results based on path length or path weight. Imagine you transferred a transportation network to a graph dataset and now navigate between two given points. With k-shortest path, you can query for shortest travel distance, shortest travel time, least amount of road fees or any other information you have stored on edges.

In the example of the European railroad connections above, we could e.g. query for the shortest distance, least stops or cheapest fare for traveling between London and Glasgow depending on the information you have stored at your edges. You can also think of various network management use cases or threat intelligence for applying the new k-shortest path feature.
If you’d like to dive a bit deeper into k-shortest paths, you can watch the video tutorial or get hands-on with the tutorial in our training center.
The new PRUNE keyword is an alternative for FILTERs in AQL graph traversal queries. Using PRUNE allows users to reduce the amount of documents the traversal query has to look up. PRUNE acts like a stop condition within graph traversals, telling the traversal to stop when a given criteria is met and return the full result path.
In contrast to pure FILTER queries, which first lookup all potential results and then apply the filter condition on all results found, PRUNE directly applies the filter condition directly to each vertex. Queries using PRUNE can, therefore, reduce the amount of total lookups needed and speed up queries significantly. By using PRUNE, internal tests show a performance gain by several orders of magnitude in some use cases. See one of these cases yourself in the video tutorial below:
Data Masking – For GDPR and CCPA-compliant Testing & Development
Testing new versions of a production environment or developing new features is best when you do so as close to production as possible. But, exporting sensitive data like names, birthdays, email addresses or credit card information from highly-secure production systems to be used in lower-security testing and development environments is often not possible -- or poses GDPR / CCPA compliance issues. Data Masking to the rescue!
The new Data Masking feature in ArangoDB lets you define sensible data to be obfuscated, then generates masked exports of these collections to be used for testing or development purposes.
The open-source edition of ArangoDB supports already a simple version of Data Masking, letting you obfuscate arbitrary data with random strings which can already be quite helpful.
But the Enterprise Edition of ArangoDB takes things a few steps further and lets you preserve the structure of the data while obfuscating it. Birthdays, credit card numbers, email addresses or other sensitive data can be defined and obfuscated in a way that preserves the structure for testing experiences as close to production as possible. Try Data Masking yourself with this tutorial.
Hot Backups – Little late to the Party (coming with 3.5.1)
Creating consistent snapshots across a distributed environment is a challenging problem.
With hot backups in the Enterprise Edition, you can create automatic, consistent backups of your ArangoDB cluster without noticeable impact on your production systems. In contrast to Arangodump, hot backups are taken on the level of the underlying storage engine and hence both backup and restore are considerably faster.
Hot backups will be available in the Enterprise Edition. Stay tuned for more details.
Neat and helpful upgrades
In addition to the new features outlined above, ArangoDB 3.5 also includes smaller improvements that add to a nice and easier experience with ArangoDB.
Sort-Limit Optimization in AQL is for specific use cases to speed up queries where it is not possible to use an index to sort the results. You can check out the tutorial with performance gain indications on our blog.
Time-to-Live Indexes allow you to automatically remove documents after a certain period of time or at a specific date. This can be useful for e.g. automatically removing session data or also with GDPR rules like “The right to be forgotten”. Check out the TTL tutorial for more details.
Index Hints allow users to provide the query optimizer with a hint that a certain index should be used. The query optimizer will then take a closer look at the index hinted. Users can also enforce the usage of a specific index. Find more details in this brief tutorial.
When using many indexes within a collection it can come in handy to name them. With Named Indexes users can now specify a name for an index to make navigating through indexes much easier. Learn how to use named indexes in this tutorial.
Of course, there are dozens of other optimizations under the hood, including performance tuning, cluster improvements and much more. Take ArangoDB 3.5 for a test drive and see for yourself. Any feedback is, as always, highly appreciated! If you are upgrading from a previous version, check our General Upgrade Guide.
Did these new features get you excited and you are curious whats next for ArangoDB? Join the “ArangoDB 3.6: The Future is Full of Features” webinar with our Head of Engineering & Machine Learning Joerg Schad.
We hope you find many useful new features and improvements in ArangoDB 3.5. If you like to join the ArangoDB Community, you can do so on GitHub, Stack Overflow and Slack.
Get the latest tutorials,
blog posts and news:
Thanks for subscribing! Please check your email for further instructions.
 Skip to content
Skip to content 

