How ArangGraphML Leverages Intel’s PyG Optimizations
ArangoGraphML + Intel: Next-level Machine Learning Accelerated
ArangoDB and Intel have announced a groundbreaking partnership to enhance Graph Machine Learning (GraphML) using Intel's high-performance processors. This collaboration, part of the Intel Disruptor Program, will seek to integrate ArangoDB's graph database solutions with Intel's Xeon CPU. This synergy promises to revolutionize data analytics and pattern recognition in complex graph structures, marking a new era in database technology and GraphML advancements.
ArangoGraphML
ArangoGraphML, part of ArangoDB's suite, is an advanced graph machine learning platform designed for efficient data analysis and pattern recognition in complex graph structures, leveraging graph database technology to drive innovation in data intelligence and analytics.
Machine Learning Performance Challenge
The quest for speed in machine learning platforms is unending. By delving into Intel’s PyG optimizations, we aim to harness the power of CPU performance enhancements specifically tailored for Graph Neural Network and PyG workloads. As ArangoGraphML is leveraging PyG, any performance improvement is relevant for us and our customers. This exploration is not only about benchmarking Intel’s PyG optimizations but also about internal testing to measure their impact on our platform.
PyG benchmark
Our focus lies on gauging the performance of GraphML algorithms within our platform using torch.compile. This method allows us to assess the efficiency gains brought about by Intel’s PyG optimizations during the training and inference time, providing insights into the tangible benefits for our users.
Benchmark methodology
To ensure a robust evaluation, we conducted tests under controlled conditions:
- System Specifications: We have used an AWS EC2 instance specifically t2.2xlarge with 8 vCPUs and 32 GiB RAM.
- Dataset: We have used ogb-products dataset which is a large-scale undirected and unweighted graph, representing an Amazon product co-purchasing network. The task is to predict the category of a product in a multi-class classification setup, where the 47 top-level categories are used for target labels. This dataset highlights its relevance to real-world scenarios.
- Batch Size, Hidden Layers, and Number of Layers: We have experimented with different essential hyper-parameters in evaluating the performance of GraphML algorithms.
The outcomes
In our preliminary assessments, we observed a noteworthy increase in performance, achieving a speedup of up to 20%. The gains were evident when comparing the execution times of GraphML algorithms with and without Intel’s PyG optimizations. The results are presented graphically in the chart below and summarized in the accompanying table.

| Batch Size | Hidden Channels | Layers | Mode | Median Time per Epoch (in seconds) | Speed up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1024 | 256 | 2 | Eager | 153.803 | |
| 1024 | 256 | 2 | Compile | 134.106 | |
| 1.15x | |||||
| 512 | 64 | 2 | Eager | 89.039 | |
| 512 | 64 | 2 | Compile | 98.714 | |
| 1.11x | |||||
| 512 | 128 | 3 | Eager | ||
| 512 | 128 | 3 | Compile | ||
| 1.12x |
Conclusion
With a demonstrated performance boost, we are now leveraging Intel’s PyG optimizations across our platform. This commitment aligns with our dedication to providing users with cutting-edge technology and optimized algorithms for their Graph Neural Network workflows.
As the field of machine learning continues to evolve, ArangoGraphML remains at the forefront, leveraging Intel’s PyTorch Geometric optimizations to ensure our users experience the fastest and most efficient ML platform available.
Stay tuned for further updates on our journey toward excellence in Graph Machine Learning!
Integrate ArangoDB with PyTorch Geometric to Build Recommendation Systems
Estimated reading time: 20 minutes
In this blog post, we will build a complete movie recommendation application using ArangoDB and PyTorch Geometric. We will tackle the challenge of building a movie recommendation application by transforming it into the task of link prediction. Our goal is to predict missing links between a user and the movies they have not watched yet.
(more…)A Comprehensive Case-Study of GraphSage using PyTorchGeometric and Open-Graph-Benchmark
Estimated reading time: 15 minute
This blog post provides a comprehensive study on the theoretical and practical understanding of GraphSage, this notebook will cover:
- What is GraphSage
- Neighbourhood Sampling
- Getting Hands-on Experience with GraphSage and PyTorch Geometric Library
- Open-Graph-Benchmark’s Amazon Product Recommendation Dataset
- Creating and Saving a model
- Generating Graph Embeddings Visualizations and Observations
ArangoML Series: Multi-Model Collaboration
Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
Multi-Model Machine Learning
This article looks at how a team collaborating on a real-world machine learning project benefits from using a multi-model database for capturing ML meta-data.
The specific points discussed in this article are how:
- The graph data model is superior to relational for ML meta-data storage.
- Storing ML experiment objects is natural with multi-model.
- ArangoML promotes collaboration due to the flexibility of multi-model.
- ArangoML provides ops logging and performance analysis.

ArangoML Series: Intro to NetworkX Adapter
Estimated reading time: 3 minutes
This post is the fifth in a series of posts introducing the ArangoML features and tools. This post introduces the NetworkX adapter, which makes it easy to analyze your graphs stored in ArangoDB with NetworkX.
In this post we:
- Briefly introduce NetworkX
- Explore the IMDB user rating dataset
- Showcase the ArangoDB integration of NetworkX
- Explore the centrality measures of the data using NetworkX
- Store the experiment with arangopipe
This notebook is just a slice of the full-sized notebook available in the ArangoDB NetworkX adapter repository. It is summarized here to better fit the blog post format and provide a quick introduction to using the NetworkX adapter.
ArangoML Part 4: Detecting Covariate Shift in Datasets
Estimated reading time: 1 minute
This post is the fourth in a series of posts introducing ArangoML and showcasing its benefits to your machine learning pipelines. Until now, we have focused on ArangoML’s ability to capture metadata for your machine learning projects, but it does much more.
In this post we:
- Introduce the concept of covariate shift in datasets
- Showcase the built-in dataset shift detection API

ArangoML Part 3: Bootstrapping and Bias-Variance
Estimated reading time: 2 minutes
This post is the third in a series of posts about machine learning and showcasing the benefits ArangoML adds to your machine learning pipelines. In this post we:
- Introduce bootstrapping and bias-variance concepts
- Estimate and analyze the variance of the model from part 2
- Capture the metadata for this activity with arangopipe

ArangoML Part 2: Streamlining Machine Learning Workflows
Estimated reading time: 1 minute
This post is the second in a series of posts about machine learning and showcasing the benefits ArangoML adds to your machine learning pipelines. In this post we:
- Introduce machine learning concepts
- Demonstrate basic model building
- Log a model building activity with arangopipe

Posts in this series:
ArangoML Part 1: Where Graphs and Machine Learning Meet
ArangoML Part 2: Basic Arangopipe Workflow
ArangoML Part 3: Bootstrapping and Bias Variance
ArangoML Part 4: Detecting Covariate Shift in Datasets
ArangoML Series: Intro to NetworkX Adapter
ArangoML Series: Multi-Model Collaboration
Hear More from the Author
What’s new in ArangoDB 3.6: OneShard Deployments and Performance Improvements
Continue Reading
What’s new in ArangoDB 3.6: OneShard Deployments and Performance Improvements
Release Candidate 2 of the ArangoDB 3.6 available for testing
ArangoML Part 1: Where Graphs and Machine Learning Meet
Estimated reading time: 4 minutes

This post is the first in a series of posts introducing ArangoML and showcasing its benefits to your machine learning pipelines. In this first post, we look at what exactly ArangoML is, with later posts in this series showcasing the different tools and use cases.
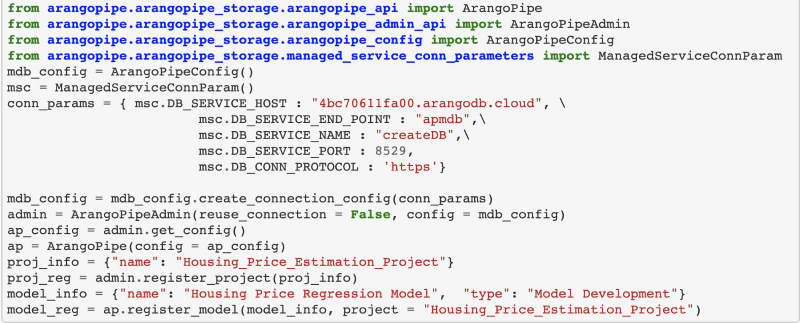
(more…)ArangoML Pipeline Cloud – Managed Machine Learning Metadata Service
Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
We all know how crucial training data for data scientists is to build quality machine learning models. But when productionizing Machine Learning, Metadata is equally important.
Consider for example:
- Capture of Lineage Information (e.g., Which dataset influences which Model?)
- Capture of Audit Information (e.g, A given model was trained two months ago with the following training/validation performance)
- Reproducible Model Training
- Model Serving Policy (e.g., Which model should be deployed in production based on training statistics)
If you would like to see a live demo of ArangoML Pipeline Cloud, join our Head of Engineering and Machine Learning, Jörg Schad, on February 13, 2020 – 10am PT/ 1pm ET/ 7pm CET for a live webinar.
This is the reason we built ArangoML Pipeline, a flexible Metadata store which can be used with your existing ML Pipeline. ArangoML Pipeline can be used as a simple extension of existing ML pipelines through simple python/HTTP APIs.
Check out this page for further details on the challenge of Metadata in Machine Learning and ArangoML Pipeline.
ArangoML Pipeline Cloud
Today we are happy to announce a first version of Managed ML Metadata. Now you can start using ArangoML Pipeline without having to even start a separate docker container.
Additionally, as a cloud-based service based on ArangoDB’s managed cloud service Oasis, it can be up & running in just a few clicks and in the Free-to-Try tier even without a lengthy registration.

If you already have an existing notebook for your Machine Learning project it is as simple as adding the ArangoML Pipeline configuration pointing to our Free-to-Try tier `arangoml.arangodb.cloud` and a dedicated environment (aka ArangoDB database with custom login credentials) will be generated for you and persisted in the config.
SLAs
ArangoML Pipeline Cloud currently comes with two different service levels:
- Free-to-Try
The Free-to-Try tier allows for a no-hassle setup as it automatically configures your own environment based on a simple API call shown above and is ideas to test ArangoML Pipeline Cloud, but comes with no guarantees for your production data. - Production
If you are considering to use ArangoML Pipeline Cloud for production setup this is- Own Oasis cluster with all of Oasis Enterprise features
- Regular Backup
- It comes with a free 14-day trial period and afterwards follows the Oasis pricing model
Please reach out to arangoml@arangodb.cloud for sign-up and details.
How to get started
To show how easy it is to get started with ArangoML Pipeline Cloud in your existing ML pipeline we have a notebook with a modified TensorFlow Tutorial example with no setup or signup required!
If you are already using ArangoML Pipeline and just want to check how to migrate to ArangoML Pipeline Cloud we suggest to take a look at the minimal minimal example notebook.
While these notebook are mostly focused on the storing of metadata, we have a number of exciting notebooks with use-cases of how to further leverage and analyze metadata including for example datashift analysis.
Learn more:
- Learn more by checking out our example notebook on Google Colab
- Checkout the examples directory in our open source repository.
- Find here a tutorial notebook to get started with ArangoML Pipeline
- Learn more about using Arangopipe with common components of a machine learning stack like Tensorflow, hyperopt and pytorch
- Learn more about ArangoML Pipeline: Visit the blog
- To join a webinar for a live demo of how ArangoML Pipeline Cloud works: Register here
Continue Reading
InfoCamere investigated graph databases and chose ArangoDB
Performance analysis with pyArango: Part III Measuring possible capacity with usage Scenarios
Milestone 2 ArangoDB 3.3 – New Data Replication Engine and Hot Standby
Get the latest tutorials,
blog posts and news:
Thanks for subscribing! Please check your email for further instructions.
 Skip to content
Skip to content