When and how to use sparse indexes in ArangoDB 2.5
This version is deprecated. Download the new version of ArangoDB
In ArangoDB 2.5, hash and skiplist indexes can optionally be made sparse.
Such sparse indexes will exclude documents in which at least one of the index attributes is either not set or has a value of null. Declaring an index as sparse can provide great savings in memory and index creation CPU time for some cases.
ArangoDB 2.5 Beta: Test New Features & Enhancements
This version is deprecated. Download the new version of ArangoDB
The current sprint comes to an end and ArangoDB 2.5 is available as beta. We appreciate your feedback and hope that many developers try this new beta release.
We have used the last weeks to improve the Foxx framework for data-centric microservices – enhancing debug capabilities, improving development-mode and the install process – to make the development of Foxx applications easier than ever.
We upgraded two main ArangoDB components, V8 and etcd to the latest versions (V8 3.31.74.1 and etcd 2.0) to support even more ES6 features and to benefit from a robust rewrite of etcd for cluster configuration.
We’ve also improved core database capabilities by adding sparse hash and skiplist indexes, dynamic attribute names and more optimizer rules. Read the full list of changes in the CHANGELOG.
ArangoDB at NoSQL Matters Paris: Insights & Innovations
If you are interested in NoSQL and come from France, the NoSQL matters conference in Paris is your place to go. ArangoDB contributes with a workshop and a talk and is a silver sponsor of the conference as well. You can meet our team at the exhibition space and ask your ArangoDB questions in person.
Tickets are available for both days, starting at €299 for the conference pass.
Anyway, come and meet us at the historical Tapis Rouge venue in the heart of Paris city!
Building Single Page Applications with Angular.JS and Foxx
Workshop on March, 26th
Angular.JS is Google’s open-source JavaScript framework optimized to build awesome single page applications. This ease of use has convinced many developers to switch. With MVC in the browser all you need from your backend is an easy way to define an API for your data.- That’s where Foxx excels.
In this training session we will build a simple single page application. Showing you how to use Angular.JS and what is a good way to define your model using Foxx.
Polyglot Persistence & Multi-Model NoSQL Databases
Talk on March, 27th (10 am)
In many modern applications the database side is realized using polyglot persistence – store each data format (graphs, documents, etc.) in an appropriate separate database. This approach yields several benefits, databases are optimized for their specific duty, however there are also drawbacks:
- keep all databases in sync
- queries might require data from several databases
- experts needed for all used systems
A multi-model database is not restricted to one data format, but can cope with several of them. In this talk i will present how a multi-model database can be used in a polyglot persistence setup and how it will reduce the effort drastically.
ArangoDB in San Francisco: Exciting Developments & Events
Join parts of the ArangoDB team in San Francisco. Max and Claudius are visiting the Bay Area from mid-February till end of March. Starting with the StrataConf in San Jose, Feb 17–20, 2015 Max and Claudius want to meet people, start cooperations, visit meetups and tell people in the Bay Area about ArangoDB.
If you know any hackerspaces we definitely should go, drop us a line and we will try to be there. We would be happy to see some of you guys in person and to respond to every question you may have about ArangoDB.
Comparison: Lockless programming with atomics in C++ 11 vs. mutex and RW-locks
ArangoDB is multithreaded and able to use several CPU-cores at once. Because of that access to common data structures to these threads have to be protected from concurrent access. ArangoDB currently uses mutexes, spinlocks and RW-locks for that. With the ongoing development of the MVCC the number of situations where protected access is needed grows significantly. If locking is done too often the scalability is effectively limited to one core. So this test was done to estimate the costs, and evaluate other solutions – so called lockless programming with atomics.
ArangoDB 2.4.3 Release: Bug Fixes and Enhancements
This version is deprecated. Download the new version of ArangoDB
A maintenance release for ArangoDB 2.4 is available for download or via your favorite package manager.
v2.4.3 (2015-02-06)
- fix multi-threading with openssl when running under Windows
- fix timeout on socket operations when running under Windows
- Fixed an error in Foxx routing which caused some apps that worked in 2.4.1 to fail with status 500:
undefined is not a functionerrors in 2.4.2 This error was occurring due to seldom internal rerouting introduced by the malformed application handler.
ArangoDB Logstash Output: Efficient Data Integration

Inspired by a question on StackOverflow, I did some investigation about how to make Logstash send log events to ArangoDB.
There is no dedicated Logstash output plugin for ArangoDB on the Logstash plugins page, so I had already accepted to write one on my own.
Browsing the plugins page for inspiration, I found an HTTP output plugin for Logstash. It seems to be general enough that it can send the log event in JSON format to any HTTP-speaking backend.
ArangoDB’s API is JSON over HTTP, so it sounded like a perfect match. I briefly tried it out and it seemed to work fine.
Dynamic Attribute Names in AQL: ArangoDB Techniques
On our mailing list, there is quite often the question whether attribute names in objects returned from AQL queries can be made dynamic. Jan discusses in his blog how such dynamic attribute names could be expressed and shows the current implementation that comes with ArangoDB 2.5 – adapting an ES6 proposal that might bring robust dynamic variable names to JavaScript as well.
In ArangoDB 2.5 you will be able to use dynamic variable names as follows:
FOR doc IN collection
LET type = doc.type;
RETURN { [type] : doc.value }
Functions are allowed as well:
FOR i IN 1..3
RETURN {
[ CONCAT('test', i) ] : i
}
ArangoDB Optimizer Rule: Efficient Calculations
In the upcoming ArangoDB 2.5 (current devel branch) a new optimizer rule move-calculations-down was added. Jan showcases in his latest blog post how queries with calculations could benefit from this new optimiser rule.
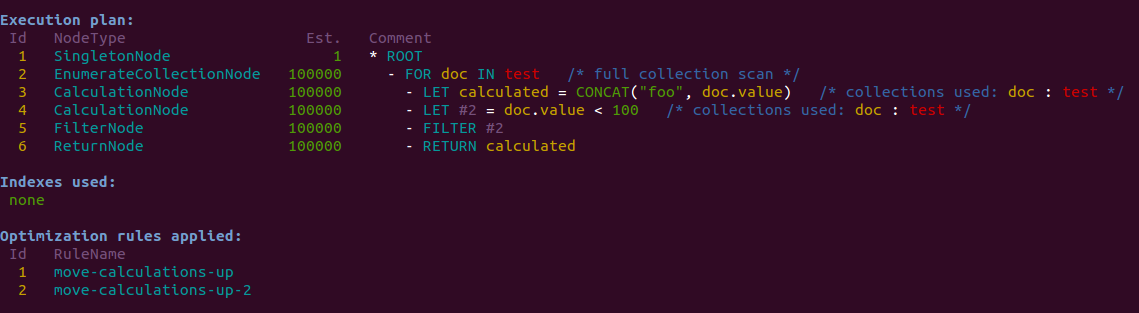
Read in Jan’s blog how this rule could accelerate your queries
ArangoDB 2.4.2
This version is deprecated. Download the new version of ArangoDB
A maintenance release for ArangoDB 2.4.2 is available for download or via your favourite package manager.
v2.4.2 (2015-01-30)
- added custom visitor functionality for AQL traversals
This allows more complex result processing in traversals triggered by AQL. A few examples are shown in this article.
- improved number of results estimated for nodes of type
EnumerateListNodeandSubqueryNodein AQL explain output
Get the latest tutorials,
blog posts and news:
Thanks for subscribing! Please check your email for further instructions.
 Skip to content
Skip to content 